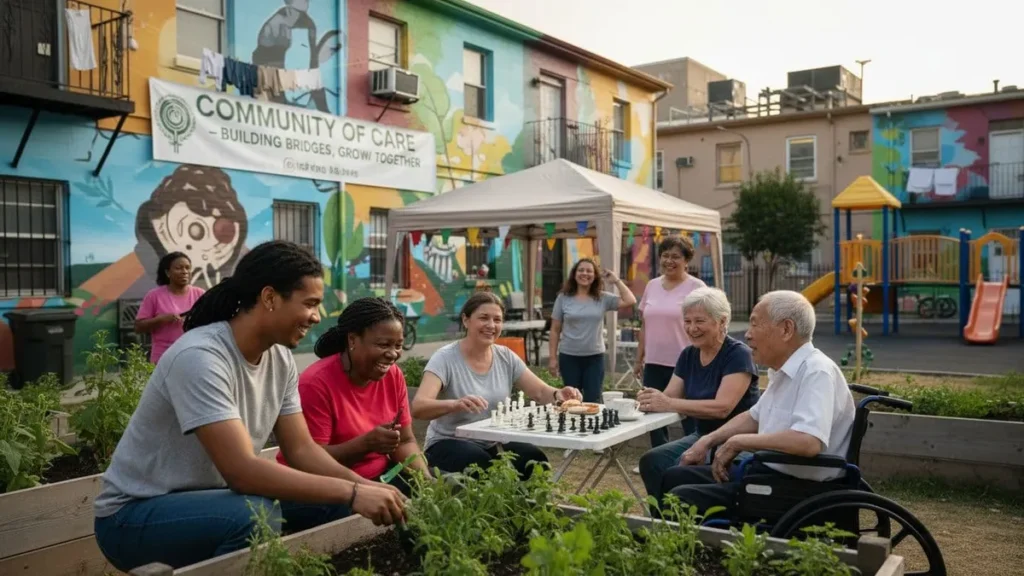Introduction
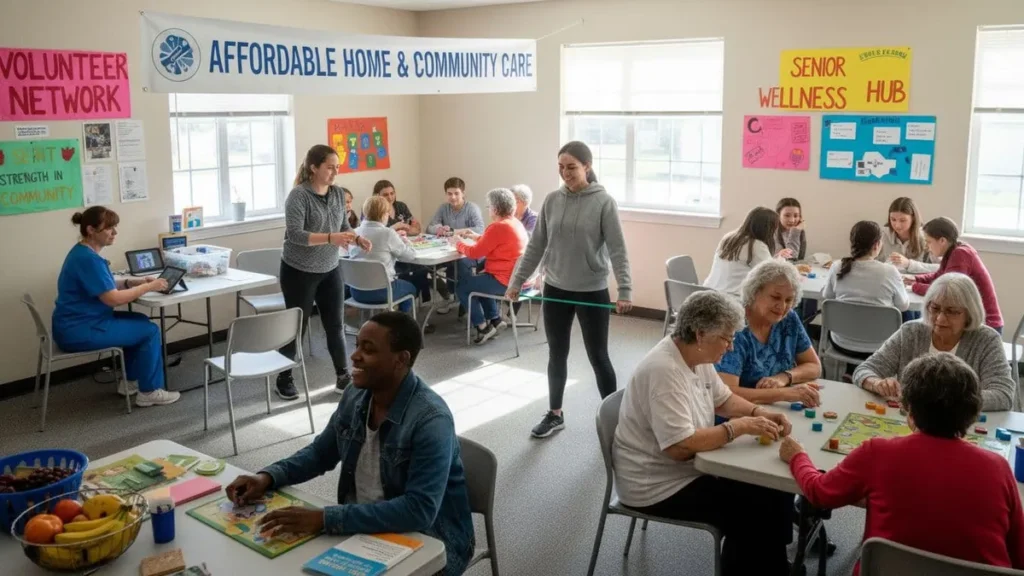
Aging gracefully is a universal desire, yet for millions of seniors in rural areas, loneliness and social isolation have become some of the most significant public health challenges of our time. As families migrate to cities in search of better opportunities, elderly individuals are often left behind, disconnected from social networks and essential care. Fortunately, community-based elder support programmes are transforming this narrative by providing companionship, care, and dignity to older adults who might otherwise be forgotten. These initiatives, powered by social workers, volunteers, and local partnerships, are creating inclusive environments where seniors rediscover purpose and belonging. In this blog, we explore how these community-led efforts reduce isolation and improve the quality of life for rural seniors worldwide.
Table of Contents
- What Are Community-Based Elder Support Programmes?
- The Rising Problem of Isolation Among Seniors in Rural Areas
- How Community-Based Programmes Work
- Role of Social Workers and Volunteers
- Benefits of Elder Support Programmes
- Technology and Innovation in Elderly Engagement
- Global Case Studies and Success Stories
- Data and Statistics
- Challenges and Sustainable Solutions
- Conclusion: Building a Connected and Compassionate Future
What Are Community-Based Elder Support Programmes?
Community-based elder support programmes are locally-driven initiatives designed to provide physical, emotional, and social care to elderly individuals, especially in rural or underserved regions. These programs combine local resources, volunteer efforts, healthcare access, and social activities to create a sense of belonging among seniors. They are often run by nonprofits, local governments, and faith-based organizations, focusing on inclusivity, companionship, and empowerment.
Common FAQs:
1. How do these programmes differ from traditional elder care?
Traditional elder care often focuses on medical or institutional settings, while community-based care emphasizes social inclusion, participation, and localized support.
2. Who manages these programmes?
Social workers, NGOs, and community leaders collaborate to design and manage initiatives tailored to local needs.
3. What services do they offer?
Services typically include home visits, group activities, healthcare monitoring, mental health support, and assistance with daily living.
4. Are they affordable for low-income communities?
Yes, most community-led programmes are cost-effective, relying on volunteerism, local donations, and nonprofit funding.
The Rising Problem of Isolation Among Seniors in Rural Areas
Social isolation among the elderly is a growing global crisis. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), nearly one in four older adults experiences social isolation, with rural seniors being most vulnerable due to geographical distance, limited transportation, and declining community engagement. Studies have linked isolation to increased risks of depression, cognitive decline, and premature mortality. In rural areas, where access to healthcare and social services is limited, community-based programmes provide an invaluable lifeline.
Isolation isn’t merely physical; it is emotional and psychological. Seniors often suffer silently, yearning for companionship and human connection. Social work interventions that focus on inclusivity and shared community experiences can significantly improve emotional health and extend life expectancy.
How Community-Based Programmes Work
Community-based elder support initiatives function through collaborative frameworks that combine local knowledge with structured social work practices. Their operational models typically include:
- Volunteer Networks: Trained community volunteers visit seniors regularly to offer companionship and practical assistance.
- Group Activities: Social gatherings, cultural events, and fitness programs that foster interaction and reduce loneliness.
- Healthcare Integration: Partnerships with local clinics for regular health check-ups, medication management, and preventive care.
- Technology Inclusion: Digital literacy programs that help seniors connect with families and participate in virtual communities.
- Peer Support: Encouraging seniors to support one another, fostering a sense of purpose and community resilience.
Role of Social Workers and Volunteers
Social workers and volunteers are the heart of community-based elder support. They serve as caregivers, advocates, and emotional anchors. Social workers assess seniors’ needs, connect them with healthcare and welfare schemes, and organize community engagement activities. Volunteers provide daily companionship and build trust within local communities. Their collective efforts ensure that care remains personal, empathetic, and culturally sensitive.
At Angel Alliance Initiatives, we emphasize collaboration between social workers and local communities to create lasting change. Every visit, every conversation, and every act of care contributes to restoring dignity and hope for rural elders.
Benefits of Elder Support Programmes
- Reduced Loneliness: Regular interactions rebuild social connections and reduce the mental health impact of isolation.
- Improved Mental and Physical Health: Seniors engaged in community activities show higher levels of happiness and lower rates of depression.
- Enhanced Safety: Regular check-ins help detect early signs of health issues or neglect.
- Economic Sustainability: Local participation and volunteerism make programmes affordable and replicable.
- Empowerment and Inclusion: Seniors are treated as valued community members, not passive recipients of aid.
These benefits extend beyond the elderly themselves—they strengthen families, enhance intergenerational bonds, and inspire youth to value empathy and service.
Technology and Innovation in Elderly Engagement
Technology has emerged as a powerful ally in combating loneliness. Even in rural areas, digital tools are connecting seniors to the world.
- Mobile Health Apps: Enable health tracking and teleconsultations.
- Virtual Communities: Platforms like WhatsApp groups and Facebook communities create digital gathering spaces.
- Voice-Assisted Devices: Tools like Alexa and Google Assistant offer companionship and safety reminders.
- Digital Literacy Training: Social workers teach seniors how to use smartphones, empowering them to reconnect with family members across distances.
These cost-effective innovations are reshaping elderly care, ensuring inclusion even in geographically isolated settings.
Global Case Studies and Success Stories
1. Japan – Ibasho Project:
In Japan, the Ibasho Project builds intergenerational spaces where elders play active roles in community decision-making, significantly reducing isolation.
2. India – HelpAge India’s Elder Helpline:
A toll-free helpline provides emotional support, legal aid, and healthcare information for rural seniors.
3. Kenya – Community Health Volunteers Network:
Local volunteers regularly visit elderly residents, offering basic healthcare and companionship, improving both physical and emotional well-being.
4. United States – Senior Corps Program:
A national initiative that connects volunteers aged 55+ with community service roles, allowing seniors to engage with peers while mentoring others.
These examples highlight how community-based approaches create sustainable and inclusive elder care ecosystems.
Data and Statistics
- 1 in 4 seniors globally suffers from social isolation, according to the WHO (2024).
- Rural elders are 30% more likely to face chronic loneliness than urban seniors.
- Participation in community programmes reduces depressive symptoms by 45% among elderly populations.
- Seniors engaged in regular volunteer-led activities show a 20% increase in life satisfaction and cognitive health.
- Over 65% of rural community programs are funded by NGOs and social enterprises, demonstrating scalability and sustainability.
Challenges and Sustainable Solutions
Challenges:
- Limited transportation and mobility options in rural areas.
- Insufficient funding for community programs.
- Cultural stigma around seeking social support.
- Lack of trained caregivers and volunteers.
Sustainable Solutions:
- Encouraging public-private partnerships to fund elder care initiatives.
- Creating mobile community hubs that reach multiple rural regions.
- Training youth and social work students to volunteer and engage with seniors.
- Launching awareness campaigns to destigmatize loneliness and promote inclusion.
Conclusion
At Angel Alliance Initiatives, we believe that no senior should ever feel invisible or forgotten. Community-based elder support programmes are not just about providing care—they are about rebuilding human connections, nurturing compassion, and honoring the wisdom of age. When communities come together to support their elderly, they strengthen their social fabric and reaffirm the values of empathy and solidarity. Every smile shared, every hand held, and every story exchanged is a step toward reducing isolation and restoring joy in the lives of seniors. Let us unite to create a world where aging is celebrated, not feared—where every elder feels seen, valued, and loved.